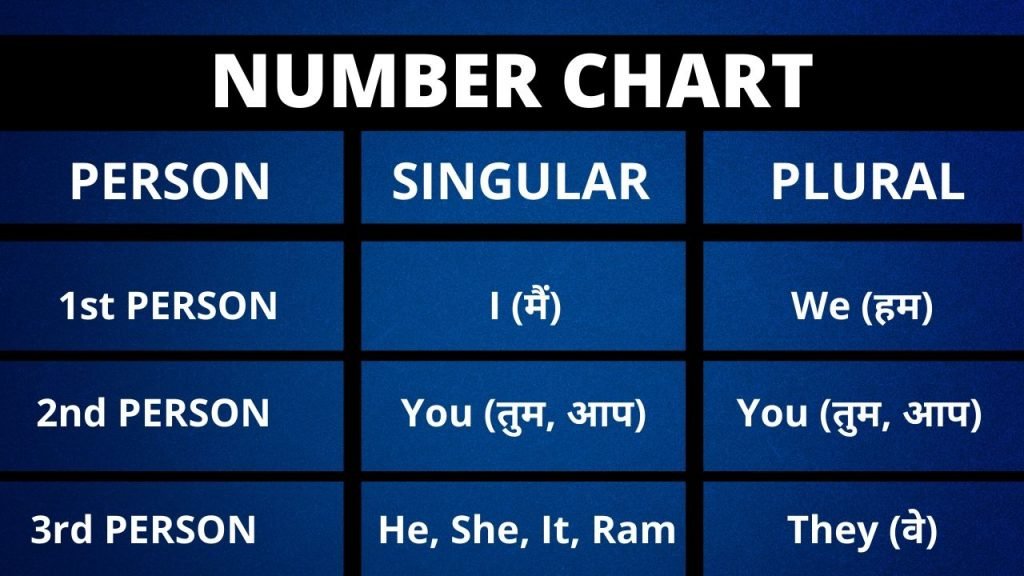
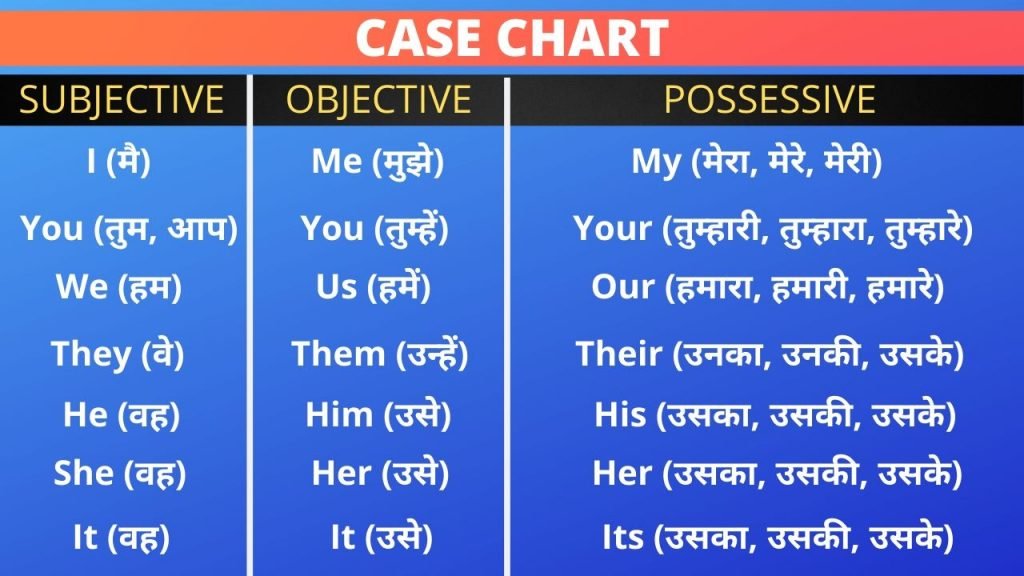
All Tenses Chart
Tense Complete Chart
Definition of Tesnes – Tense is used to show the time at which the action of a verb takes place.
In all languages, tense is divided into three classes namely –
1. Present Tense
2. Past Tense
3. Future Tense
Each of these tenses is further divided into four classes –
Present Tense
- Present Simple Tense
- Present Continuous Tense
- Present Prefect Tense
- Present Prefect Continuous Tense
Past Tense
- Past Simple Tense
- Past Continuous Tense
- Past Perfect Tense
- Past Perfect Continuous Tense
Future Tense
- Future Indefinite Tense
- Future Continuous Tense
- Future Perfect Tense
- Future Perfect Continuous Tense
Here we included 15 best tense charts with their definition, types and structure with examples –
1. Present Indefinite Tense
Note 1 – With Third Person Singular subjects (He, She, It, or any name), s, es, or ies is added to the main verb.
Note 2 – While making Negative and Interrogative sentences, do is used with I, We, You, They, and plural subjects, whereas does is used with He, She, It, or any Third Person Singular subject.
2. Present Continuous Tense
Note – While making Negative sentences, Not is used after the auxiliary verb.
3. Present Perfect Tense
Note – While making Negative sentences:
Subject + Have/Has + Not + rest of the sentence.
While making Interrogative sentences:
Have/Has + Subject + rest of the sentence + ?
4. Present Perfect Continuous Tense
Note – Since is used for a specific point of time – e.g., since morning, since evening, since last night, since past days, since March, since 2 PM, since 2008.
For is used for a period of time / duration – e.g., for 4 days, for 2 years, for 10 months, for 10 hours, for 5 minutes, for March 2008.
5. Past Indefinite Tense
In this tense, while making Negative and Interrogative sentences, the helping verb “Did” is used.
6. Past Continuous Tense
Note – With I or He, She, It (third person singular subject) use was, and with We, You, They (plural subject) use were.
7. Past Perfect Tense
Note – In this tense, the auxiliary verb Had is used with all subjects.
For making Negative and Interrogative sentences, the remaining rules remain the same.
8. Past Perfect Continuous Tense
Note – In all subjects, the auxiliary verb Had Been is used.
In Negative sentences:
Sub. + Had + Not + Been + Rest of the sentence
In Interrogative sentences:
Had + Sub. + Been + Rest of the sentence
Use Since for definite time and For for indefinite time.
9. Future Indefinite Tense
Note – With I and We, the auxiliary verb Shall is used, and with all other subjects, the auxiliary verb Will is used.
10. Future Continuous Tense
Note – In negative sentences, use Sub. + shall not be or will not be, and the rest of the sentence remains unchanged.
In interrogative sentences, use Shall/Will + Sub. + be, and the rest of the sentence remains unchanged.
11. Future Perfect Tense
Note – In negative sentences, use Sub. + shall not have / will not have, and the rest of the sentence remains unchanged.
In interrogative sentences, use Shall/Will + Sub. + have + the rest of the sentence unchanged.
12. Future Perfect Continuous Tense
Note – In negative sentences, use Sub. + will/shall + not + have been, and the rest of the sentence remains unchanged.
In interrogative sentences, use Shall/Will + Sub. + have been + the rest of the sentence, followed by a question mark. All other rules remain the same.